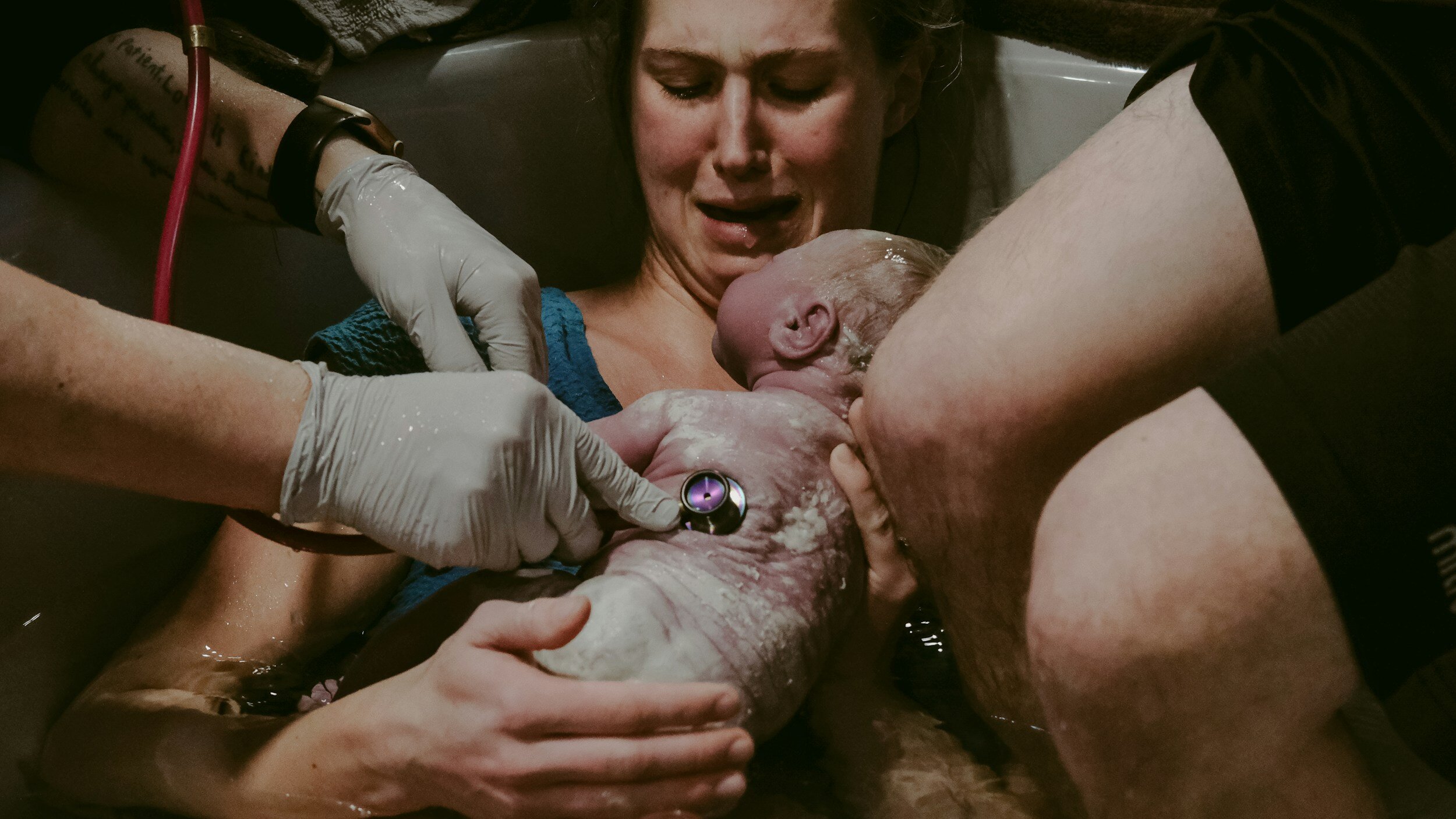
Midwives
A midwife is a trained health professional who provides care and support to individuals during pregnancy, labor, childbirth, and the postpartum period. Midwives offer prenatal care, assist during labor and delivery, and provide guidance and support for breastfeeding and newborn care. They focus on providing personalized, holistic care that emphasizes the physical, emotional, and social well-being of both the birthing person and the baby. Midwives may work in various settings, including hospitals, birth centers, or attend home births, depending on their training and the preferences of the individuals they serve.
-

Sage Willow Midwifery & Wellness

Search by Location
Frequently Asked Questions
-
A homebirth midwife is a healthcare provider who specializes in providing prenatal, labor, birth, and postpartum care for pregnant individuals who choose to give birth at home rather than in a hospital or birth center. Homebirth midwives are trained and experienced in delivering babies in non-hospital settings, and they work to ensure the safety and well-being of both the birthing person and the baby during the home birth process.
Here are some key aspects of homebirth midwives care:
Training and Certification: Homebirth midwives can have various levels of training and certification depending on the country or state in which they practice. In the United States, Certified Professional Midwives (CPMs) are midwives specifically trained to attend home births and have earned national certification. Certified Nurse-Midwives (CNMs) may also provide homebirth services in some states.
Prenatal Care: Homebirth midwives provide comprehensive prenatal care, which includes regular check-ups, monitoring the pregnancy's progress, and discussing birth plans with the expectant parents. They may offer dietary guidance, recommend tests, and provide emotional support.
Home Birth Preparation: Homebirth midwives help prepare the home for the birth, ensuring that necessary equipment and supplies are available. They also assist parents in creating a birth plan and making informed choices about their birth preferences.
Labor and Birth Support: During labor and birth, homebirth midwives provide continuous care and support. They monitor the progress of labor, assist with pain management techniques, and ensure that the birthing person and baby are safe throughout the process.
Emergency Preparedness: Homebirth midwives are trained to handle emergencies that may arise during childbirth at home. They carry equipment and medications to address potential complications and have a plan for transferring care to a hospital if necessary.
Postpartum Care: After the birth, homebirth midwives provide postpartum care for both the birthing person and the baby. This includes checking the baby's health, assessing the birthing person's recovery, and providing guidance on breast/chestfeeding and postpartum care.
Emphasis on Informed Choice: Homebirth midwives often prioritize informed decision-making, ensuring that parents are educated about their options and actively participate in the birth process. They aim to create a supportive and empowering birthing experience.
Homebirth midwives work in collaboration with other healthcare providers and may have established protocols for transferring care to a hospital in case of complications or emergencies. The safety and well-being of both the birthing person and the baby are their primary concerns during a home birth.
-
The coverage of homebirth midwives by insurance in Vermont could vary depending on the specific insurance plan and provider. Coverage for homebirth midwives is influenced by state regulations, individual insurance policies, and the type of midwife providing care (Certified Professional Midwives or Certified Nurse-Midwives).
Here are some factors to consider regarding insurance coverage for homebirth midwives in Vermont:
Certified Professional Midwives (CPMs): Vermont licenses and regulates Certified Professional Midwives (CPMs) who can legally attend home births in the state. Some insurance plans may cover services provided by CPMs, while others may not.
Certified Nurse-Midwives (CNMs): Certified Nurse-Midwives, who are trained as advanced practice registered nurses (APRNs), may also provide homebirth services in Vermont. CNMs often have more extensive insurance coverage for their services compared to CPMs.
State Laws and Regulations: Vermont has laws and regulations related to homebirth, and these can impact insurance coverage. It's important to understand both state and insurance company policies.
In-Network vs. Out-of-Network: Insurance coverage may be more comprehensive for services provided by in-network providers. It's advisable to check with your insurance company to determine whether your chosen homebirth midwife is in-network.
Preauthorization: Some insurance plans may require preauthorization for homebirth services. It's essential to contact your insurance company and follow their procedures to ensure that coverage is in place.
Out-of-Pocket Costs: Even if insurance covers homebirth midwife services, there may still be out-of-pocket costs, such as paying for the midwifery birthing assistant, deductibles, co-payments, or co-insurance. Be sure to understand the financial aspects of your insurance coverage.
Since insurance policies and regulations can change over time, we recommend contacting your specific insurance provider directly to inquire about coverage for homebirth midwives in Vermont. Additionally, you may want to consult with the homebirth midwife you are considering hiring, as they may have experience working with various insurance plans and can provide guidance on navigating the insurance process.
-
There are several types of midwives who provide care to individuals during pregnancy, labor, childbirth, and the postpartum period:
Certified Nurse-Midwives (CNMs): These midwives are registered nurses with additional training in midwifery. They are licensed to provide a wide range of healthcare services, including prenatal care, childbirth assistance, and gynecological care.
Certified Midwives (CMs): Similar to CNMs, certified midwives are non-nurse midwives who have completed a midwifery education program accredited by the Accreditation Commission for Midwifery Education (ACME). They are certified to provide midwifery care but may not have a background in nursing.
Certified Professional Midwives (CPMs): CPMs are trained specifically in out-of-hospital birth settings, such as home births and birth centers. They are certified through the North American Registry of Midwives (NARM) and primarily focus on supporting individuals who prefer to give birth outside of a hospital setting.
Direct-Entry Midwives: Direct-entry midwives are trained in midwifery through various routes that do not involve nursing education. They may include CPMs, traditional midwives, and other non-nurse midwives who have received formal training in midwifery care.
These types of midwives may work independently or as part of a healthcare team, and they provide personalized care to individuals throughout the childbirth experience.
-
People choose midwifery care for a variety of reasons, including:
Personalized and holistic care: Midwives typically provide individualized care that considers the physical, emotional, and social needs of the person giving birth, as well as their family.
Continuity of care: Many people appreciate the consistent support and guidance offered by midwives throughout the pregnancy, labor, childbirth, and postpartum periods.
Focus on physiologic childbirth: Midwives often support physiologic childbirth options and empower people to make informed decisions about their birthing experience, including options for pain management and labor interventions.
Respect for cultural and personal preferences: Midwives often take a collaborative approach to care, respecting the cultural and personal beliefs of the individuals they serve and involving them in decision-making processes.
Homebirth or alternative birth settings: For those who prefer to give birth at home or in a birth center, midwives offer specialized care and support in these settings.
Lower rates of medical interventions: Studies have shown that midwifery care is associated with lower rates of interventions such as cesarean sections, epidurals, and episiotomies, which can be appealing to people seeking a unmedicated childbirth experience.
Overall, people choose midwifery care for its focus on personalized, holistic, and empowering approaches to childbirth that align with their values and preferences.
